(fix): update pylint tutorial link and link text (#3748)
This commit is contained in:
@@ -10,8 +10,7 @@ You should also install the following `pytest` plugins:
|
||||
We also recommend using the code linting program [pylint][pylint], as it is part of our automated feedback on the website and can be a very useful static code analysis tool.
|
||||
For ease-of-use, the [pytest-pylint][pytest-pylint] plugin for `pytest` will allow you to run `pylint` via `pytest` on the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Pylint configuration can be a bit much, so this [tutorial from pycqa.org][tutorial from pycqa.org] can be helpful for getting started, as can this overview of [Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices][Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices] from Real Python.
|
||||
|
||||
Pylint configuration can be a bit much, so this [tutorial from pylint.readthedocs.io][tutorial from pylint.readthedocs.io] can be helpful for getting started, as can this overview of [Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices][Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices] from Real Python.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing pytest
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +24,6 @@ Please adjust the install commands below accordingly.
|
||||
To install `pytest` in a virtual environment, ensure the environment **is activated** prior to executing commands.
|
||||
Otherwise, the `pytest` installation will be global.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Windows
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +39,6 @@ Successfully installed pytest-7.2.2 ...
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To check if installation was successful:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
@@ -85,7 +82,6 @@ More information on pytest marks can be found in the `pytest` documentation on [
|
||||
|
||||
_More information on customizing pytest configurations can be found in the pytest documentation on [configuration file formats][configuration file formats]_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Test Failures
|
||||
|
||||
When tests fail, `pytest` prints the text of each failed test, along with the expected and actual `return` values of each to the terminal.
|
||||
@@ -110,7 +106,6 @@ FAILED exercise_test.py::ExerciseTest::name_of_failed_test
|
||||
|
||||
If you really want to be specific about what pytest returns on your screen, here are some handy command-line arguments that allows you to configure its behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Return All Details [`-v`]
|
||||
|
||||
Adding the `-v` (_verbose_) flag will return both environment information and a test summary in addition to test failures:
|
||||
@@ -166,7 +161,6 @@ FAILED example_test.py::ExampleTest::example_test_foo
|
||||
The `pytest-cache` plugin remembers which tests failed last time you ran `pytest`, so using the flag `--ff` will tell `pytest` to run previously failed tests **first**, then continue with the remainder of the tests.
|
||||
This might speed up your testing if you are making a lot of smaller fixes around one particular task or set of inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$(my_venv) python3 -m pytest -o markers=task --ff <example_file_test.py>
|
||||
==================== 7 passed in 503s ====================
|
||||
@@ -192,7 +186,6 @@ This will test your solution.
|
||||
When `pytest` encounters a failed test, the program will stop and tell you which test failed.
|
||||
When you make fixes and run the test again, `pytest` will first run the previous test that failed, then continue with the remaining tests.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Using PDB, the Python Debugger, with pytest
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to "debug like a pro", you can use the `--pdb` argument after the `pytest` command, and drop into the built-in [Python debugger][pdb], `PDB`.
|
||||
@@ -206,13 +199,11 @@ When a test fails, dropping into `PDB` will allow you to step through your code
|
||||
More details on the `PDB` module can be found in the [Python documentation on PDB][pdb].
|
||||
Additionally, the [pytest docs on PDB][pytest-pdb] and [this guide from Real Python](https://realpython.com/python-debugging-pdb/) are extremely helpful.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Extending your IDE
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like to extend your IDE with some tools that will help you with testing and improving your code, check the [tools](./tools) page.
|
||||
We explore multiple IDEs, editors and some useful extensions for linting and debugging there.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional information
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding python to your PATH
|
||||
@@ -245,7 +236,6 @@ Then add a new line, as shown in the picture, replacing `{python_directory}` wit
|
||||
|
||||
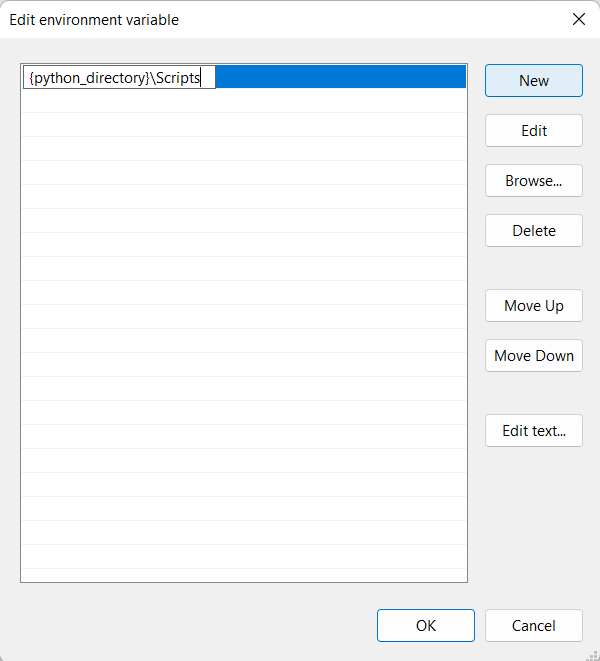
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### MacOS/Linux
|
||||
|
||||
The below should work for most Linux and MacOS flavors with a `bash` shell.
|
||||
@@ -264,13 +254,13 @@ export PATH=”$PATH:{python_directory}}”
|
||||
[pip]: https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/getting-started/
|
||||
[psf-installer]: https://www.python.org/downloads/
|
||||
[pylint]: https://pylint.pycqa.org/en/latest/user_guide/
|
||||
[pytest-cache]:http://pythonhosted.org/pytest-cache/
|
||||
[pytest-cache]: http://pythonhosted.org/pytest-cache/
|
||||
[pytest-pdb]: https://docs.pytest.org/en/6.2.x/usage.html#dropping-to-pdb-python-debugger-on-failures
|
||||
[pytest-pylint]:https://github.com/carsongee/pytest-pylint
|
||||
[pytest-subtests]:https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-subtests
|
||||
[pytest-pylint]: https://github.com/carsongee/pytest-pylint
|
||||
[pytest-subtests]: https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-subtests
|
||||
[pytest.ini]: https://github.com/exercism/python/blob/main/pytest.ini
|
||||
[python command line]: https://docs.python.org/3/using/cmdline.html
|
||||
[python-m-pip]: https://snarky.ca/why-you-should-use-python-m-pip/
|
||||
[quick-and-dirty]: https://snarky.ca/a-quick-and-dirty-guide-on-how-to-install-packages-for-python/
|
||||
[tutorial from pycqa.org]: https://pylint.pycqa.org/en/v2.17.2/tutorial.html
|
||||
[tutorial from pylint.readthedocs.io]: https://pylint.readthedocs.io/en/v2.17.7/tutorial.html
|
||||
[working with custom markers]: https://docs.pytest.org/en/6.2.x/example/markers.html#working-with-custom-markers
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user