When installing pytest or any other module(s), make sure that you have [activated your environment](.\TOOLS.md#activating-your-virtual-environment). After which you can run:
To run the tests, go to the folder where the exercise is stored using `cd` in your terminal (_replace `{exercise-folder-location}` below with the path_).
When your code returns an incorrect or unexpected value, pytest returns all the failed tests and the returned and expected values of each. Look at the following failed test file:
Running the `pytest -x {exercise_test.py}` command, will run the tests like normal, but will stop the tests after the first failed test. This will help when you want to debug a single failure at a time.
`pytest-cache` remembers which tests failed last time you ran `pytest`, running `pytest --ff {exercise_test.py}` will run those previously failed tests first, then it will continue with the rest of the tests. This might speed up your testing if you are making a lot of smaller fixes.
This will test your solution. When `pytest` encounters a failed test, the program will stop and tell you which test failed. When you run the test again, `pytest` will first test that failed test, then continue with the rest.
When a test fails, `PDB` allows you to look at variables and how your code responds. If you want to learn how to use the `PDB` module, have a look at the [Python Docs](https://docs.python.org/3/library/pdb.html#module-pdb) or [this](https://realpython.com/python-debugging-pdb/) Real Python article.
If you'd like to extend your IDE with some tools that will help you with testing and improving your code, check the [TOOLS](./TOOLS.md) page. We go into multiple IDEs, editors and some useful extensions.
**Note:** If you are running a [virtual environment](.\TOOLS.md) you do not need to *add to path* as it should work fine.
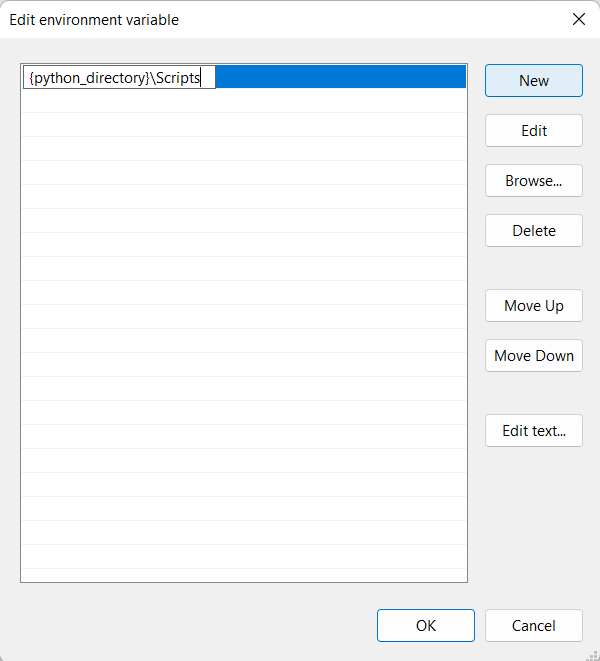
Typing `python3 -m` every time you want to run a module can get a little annoying. You can add the `Scripts` folder of your Python installation to your path. If you do not know where you have installed Python, run the following command in your terminal:
Click the `Windows Start` button and lookup *Edit the system environment variables* and press enter. Next press, `Environment Variables...`:
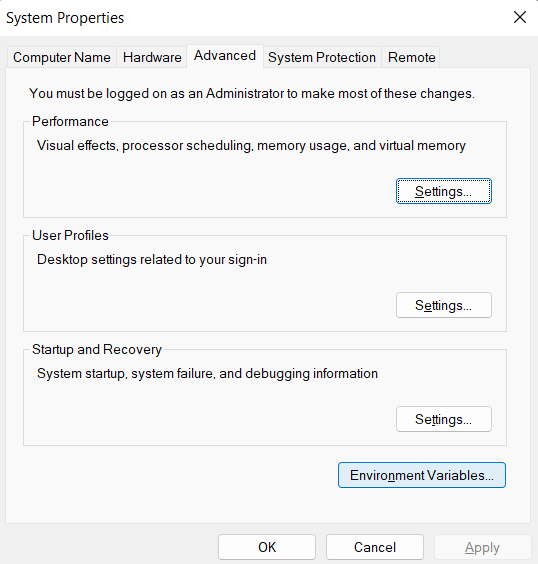
Then find the `Path` variable in your *User variables*, select it, and click `Edit...`:
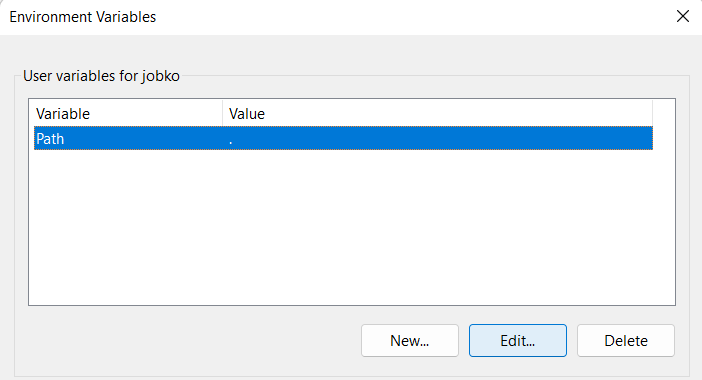
Then add a new line, as shown in the picture, replacing `{python_directory}` with your Python installation's directory:
### Fixing warnings
It is possible that you will get `warnings` about "unknown markers" when running a test that uses our _new_ syntax.
To resolve this issue, we use a `pytest.ini` file, which can be downloaded from the top level of the Python track directory: [pytest.ini](https://github.com/exercism/python/blob/main/pytest.ini).
You can also create your own file with the following content: